BPMN Designer
Use the Flowset BPMN Designer to edit BPMN diagrams in IntelliJ IDEA. The BPMN Designer will appear when you open an existing .bpmn file. If you create a new diagram via Flowset Studio, it will open automatically in the Designer.
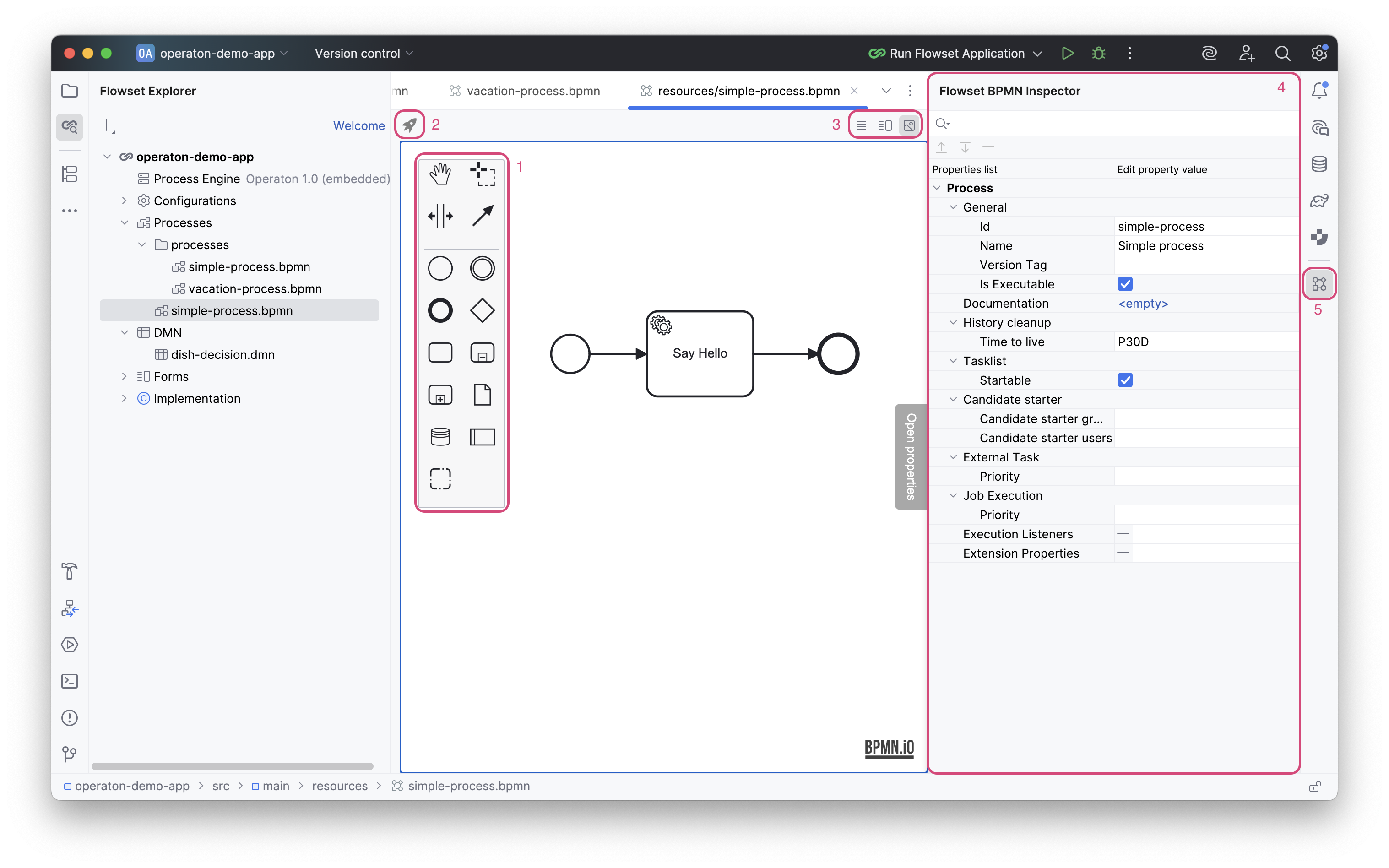
The BPMN designer interface consists of:
Canvas |
Workspace for creating a process diagram. |
|
BPMN Palette |
(1) |
The BPMN Palette provides a complete set of elements for building BPMN diagrams. |
Process Actions |
(2) |
Panel of available actions for the process. |
Editor Modes |
(3) |
Panel for selecting the view mode. Three view modes are available: XML only, XML and model, model only. |
BPMN Inspector |
(4) |
The inspector panel displays the attributes of the selected element and allows editing them. |
Visibility Button |
(5) |
Visibility toggle for the inspector. |
BPMN Editor
The BPMN editor allows building processes directly in the IDE.
|
The feature to run the JCEF browser in a separate process was implemented in IntelliJ IDEA 2025.1+ to improve stability (so that browser issues do not affect the main IDEA process). However, currently, there are a number of unresolved problems that interfere with the JCEF browser’s operation. Flowset Studio disables this option by default. This is a necessary measure for stable JCEF operation until JetBrains releases an appropriate patch. This option is available for editing in Settings: Language & Frameworks | Flowset → Enable JCEF in separate process. |
Basic Operations
Add Element |
Two methods:
|
Change Element Type |
|
Change Element Fill Color |
|
Delete Element |
|
Properties Panel (BPMN Inspector)
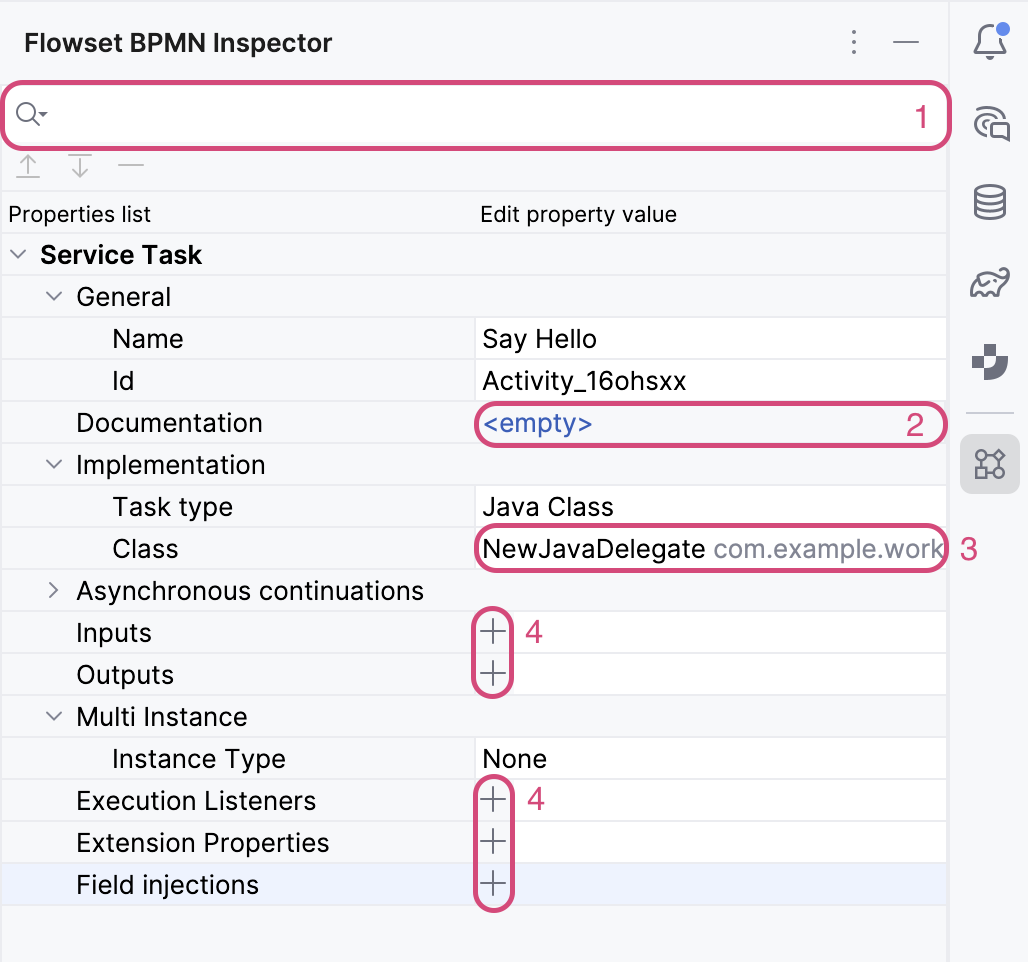
The properties panel allows changing the parameters of the selected diagram element. If no element is selected, the process properties are displayed.
Search |
(1) |
Search for an attribute by name; clicking the icon shows a dropdown search history. |
<empty> link |
(2) |
Opens a dialog for editing multi-line text. If text is already set, the first line is displayed as a link. |
|
(3) |
Opens a drop-down list of available options. |
|
(3), (4) |
Opens a dialog for setting a property (Inputs, Outputs, Field injection, etc.) or a wizard for generating an element (Java Delegate, Execution Listeners, etc.) |
|
(3) |
Navigation to code. |
Selecting User Form / DMN / Java Delegate from drop-down list
The BPMN Inspector allows selecting existing project forms, tables, and classes from the corresponding drop-down lists in the properties.
User Form |
|
DMN |
|
Java Delegate |
|
Generating Task Listener / Execution Listener
Flowset Studio allows generating Task Listener and Execution Listener class templates.
Step 1. Select an element on the process diagram
Step 2. Click the + icon in the Execution Listeners or Task Listeners field (for User Task)
Task Listener |
Execution Listener |
|
|
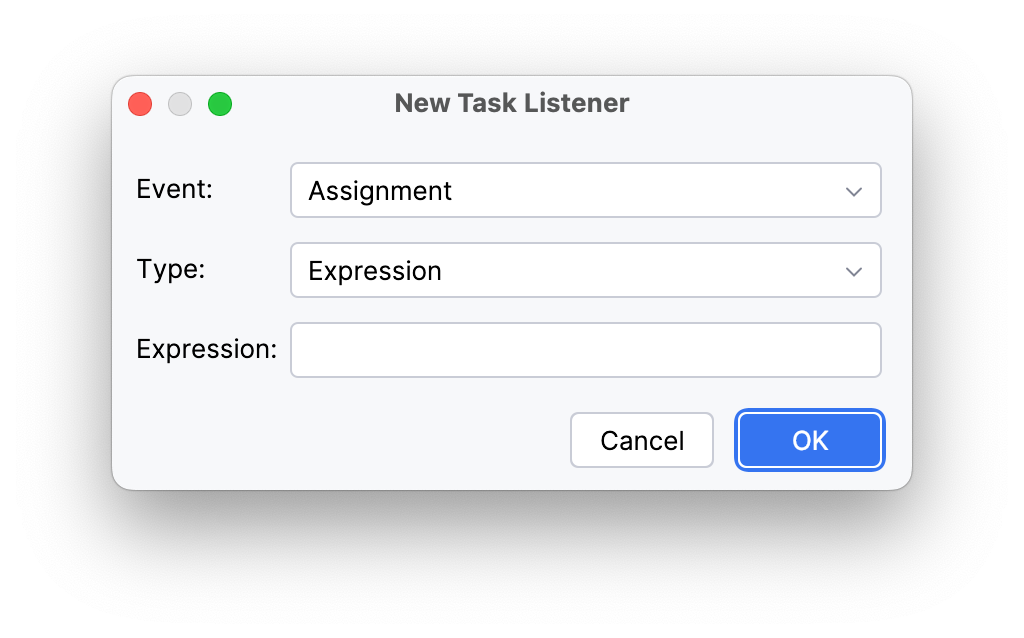
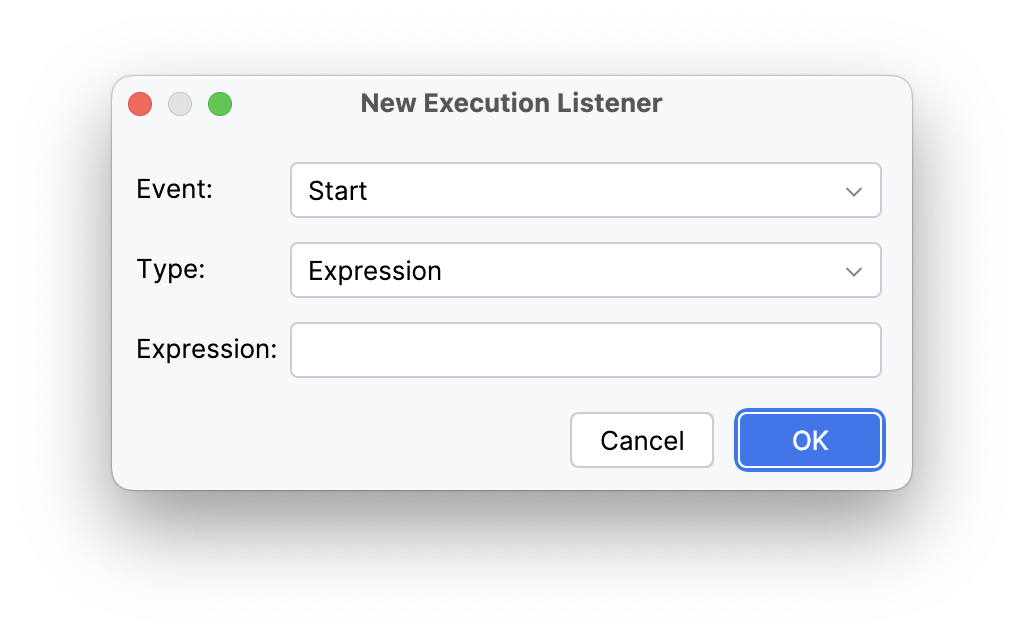
Step 3. Specify the value for the Event parameter:
Task Listener |
Assignment |
The event occurs when a task is assigned to a user or group. Used for sending notifications or logging the assignment. |
Create |
Generated after a task instance is created. Used for initializing variables, setting deadlines, or preparing data. |
|
Complete |
Called when a user completes a task. Intended for post-processing: updating data, starting the next process steps, or logging results. |
|
Delete |
Occurs when a task is deleted (e.g., when a process is interrupted). Used for releasing resources or canceling related actions. |
|
Execution Listener |
Start |
Occurs when a process element starts (e.g., process start, activity, or transition). The listener performs variable initialization or logs the operation start. |
End |
Occurs when a process element ends (e.g., activity or process end). Used for cleaning up resources, committing results, or updating statuses. |
|
Take |
Activated when passing through a sequence flow (transition). Used for tracking the process execution path or validating transition conditions. |
Step 4. Specify the type of Task Listener / Event Listener to generate:
Java class |
Direct specification of a class implementing the ExecutionListener interface. The full class name must be available in the classpath. Used for complex logic requiring full Java code. |
Expression |
An expression to be executed when the event occurs. A DelegateTask object and the event name (using |
Delegate expression |
A reference to a bean (e.g., a Spring Bean) implementing the ExecutionListener interface. Specified in the format |
If the Expression type is selected, a field for entering the expression becomes available.
If the Java class or Delegate expression type is selected, the following actions are available:
-
Select an existing class from the drop-down list (
vicon) -
Create a new class (
+icon)
Clicking the + icon invokes the wizard for creating a new Execution Listener / Task Listener:
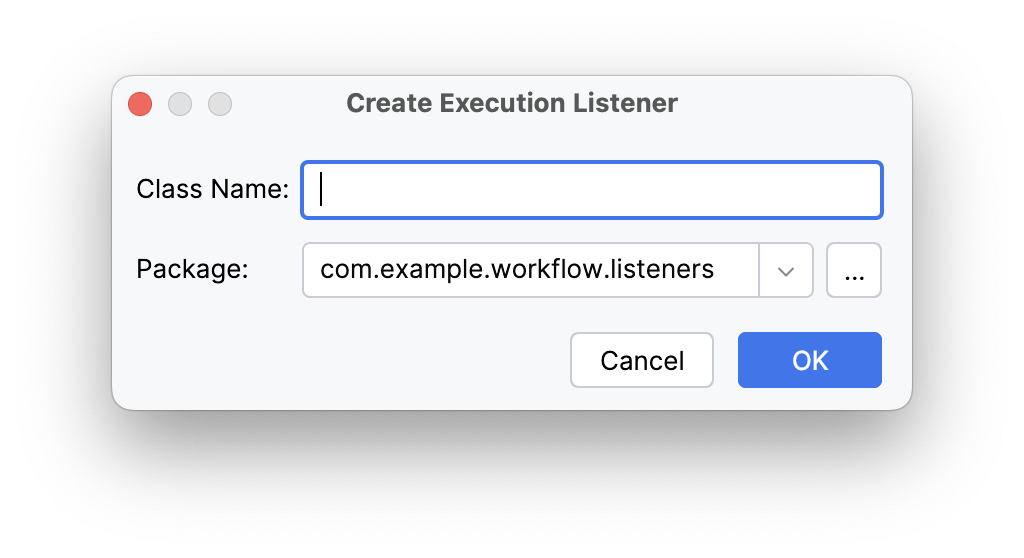
Class Name |
Name of the generated class |
Package |
Package where the generated class will be placed |
Clicking the OK button will create the class in the specified package, and the Listener Class field of the New Execution Listener (or New Task Listener) dialog will be filled.
Generating Java Delegate
The BPMN Inspector allows invoking the wizard for generating a Java Delegate class.
-
Select a Service Task on the diagram
-
Set Implementation → Task Type to Java Class
-
Click in the Class field to display the control elements
-
Click the
+icon in the field to invoke the dialog for generating a Java Delegate class
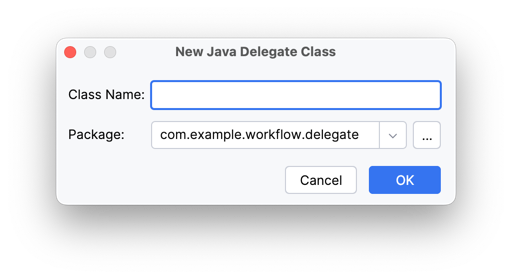
Class Name |
Name of the generated class |
Package |
Package where the generated class will be placed |
Clicking the OK button will open the generated class in the code editor.
Deployment
The BPMN editor allows deploying the process to a remote Camunda/Operaton engine. To invoke the deployment wizard, click the rocket icon in the Editor Toolbar. A correctly configured connection to an external engine is required.
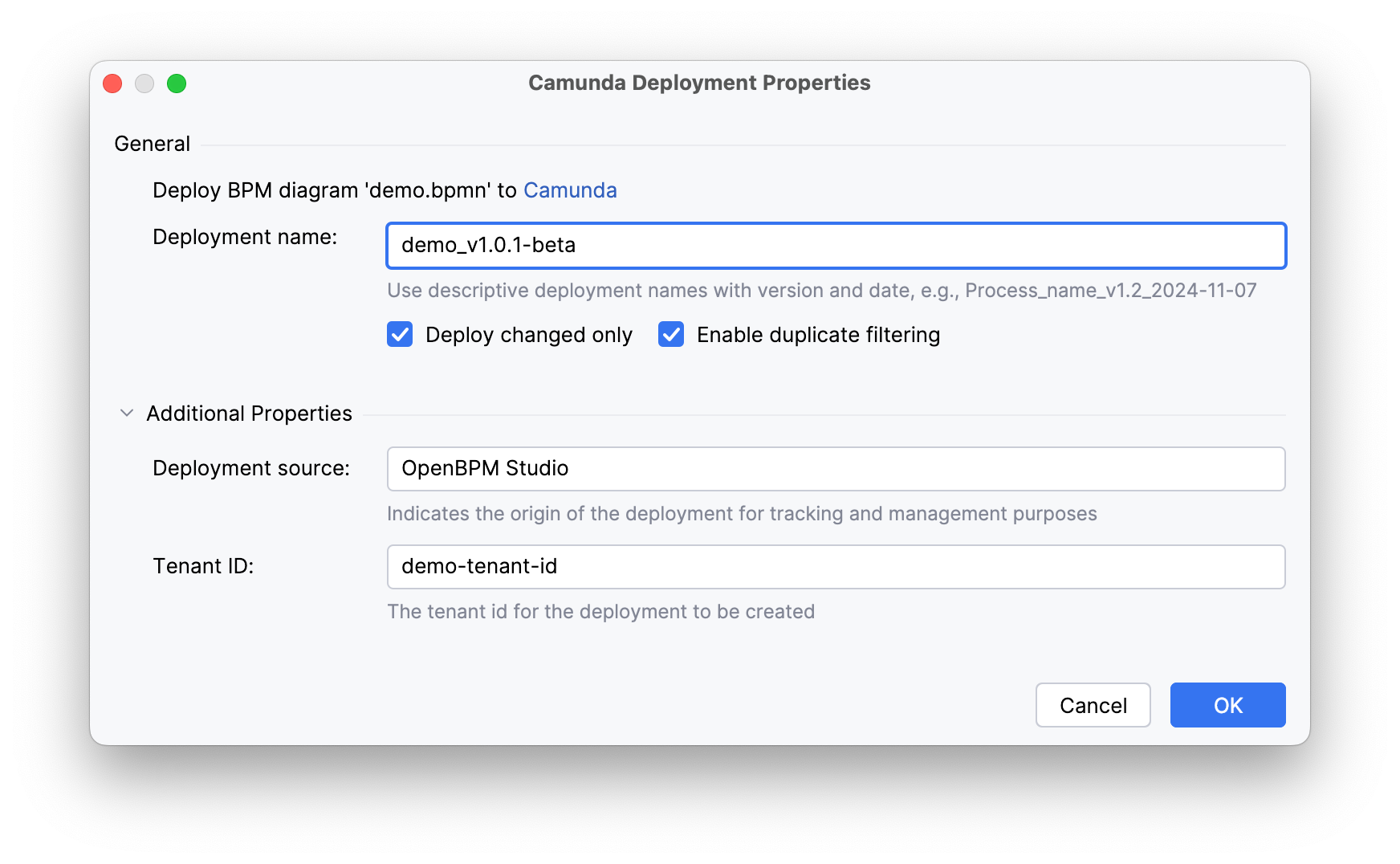
Deployment name |
A unique name for identifying the deployment package. Allows easy finding and administration of a specific process version in the system. |
Enable duplicate filtering |
Filtering at the individual file level. Skips redeployment of unchanged resources (e.g., BPMN diagrams) within a deployment. Saves database space by preventing duplicate creation. |
Deploy changed only |
Filtering at the entire deployment package level. If no file in the deployment has changed, the operation is entirely ignored. Ensures idempotence, excluding unnecessary process version creations. |
Deployment source |
The source from which the deployment was initiated (e.g., 'Flowset Studio'). Used for auditing and tracking deployment origins. |
Tenant ID |
The tenant identifier for a multi-tenant architecture. Allows isolating processes and data for different clients or departments within a single Camunda cluster. |